At $45.53, Is Yirendai Ltd (YRD) A Buy?

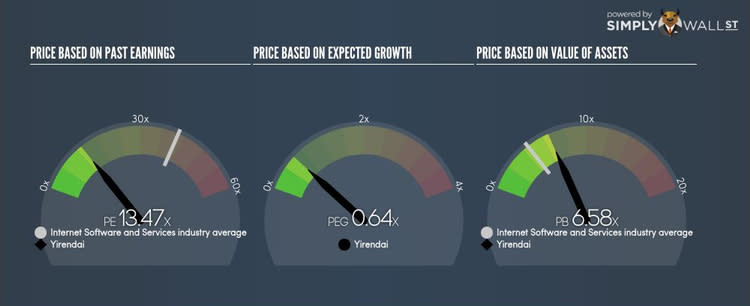
Yirendai Ltd (NYSE:YRD) trades with a trailing P/E of 13.5x, which is lower than the industry average of 40.1x. While YRD might seem like an attractive stock to buy, it is important to understand the assumptions behind the P/E ratio before you make any investment decisions. In this article, I will deconstruct the P/E ratio and highlight what you need to be careful of when using the P/E ratio. Check out our latest analysis for Yirendai
Demystifying the P/E ratio
A common ratio used for relative valuation is the P/E ratio. It compares a stock’s price per share to the stock’s earnings per share. A more intuitive way of understanding the P/E ratio is to think of it as how much investors are paying for each dollar of the company’s earnings.
P/E Calculation for YRD
Price-Earnings Ratio = Price per share ÷ Earnings per share
YRD Price-Earnings Ratio = 45.53 ÷ 22.489 = 13.5x
On its own, the P/E ratio doesn’t tell you much; however, it becomes extremely useful when you compare it with other similar companies. We preferably want to compare the stock’s P/E ratio to the average of companies that have similar features to YRD, such as capital structure and profitability. A quick method of creating a peer group is to use companies in the same industry, which is what I will do. Since YRD's P/E of 13.5x is lower than its industry peers (40.1x), it means that investors are paying less than they should for each dollar of YRD's earnings. As such, our analysis shows that YRD represents an under-priced stock.
A few caveats
Before you jump to the conclusion that YRD is the perfect buying opportunity, it is important to realise that our conclusion rests on two assertions. The first is that our “similar companies” are actually similar to YRD, or else the difference in P/E might be a result of other factors. For example, if you compared lower risk firms with YRD, then investors would naturally value it at a lower price since it is a riskier investment. The second assumption that must hold true is that the stocks we are comparing YRD to are fairly valued by the market. If this does not hold, there is a possibility that YRD’s P/E is lower because our peer group is overvalued by the market.
What this means for you:
Are you a shareholder? If your personal research into the stock confirms what the P/E ratio is telling you, it might be a good time to add more of YRD to your portfolio. But keep in mind that the usefulness of relative valuation depends on whether you are comfortable with making the assumptions I mentioned above.
Are you a potential investor? If you are considering investing in YRD, looking at the PE ratio on its own is not enough to make a well-informed decision. You will benefit from looking at additional analysis and considering its intrinsic valuation along with other relative valuation metrics like PEG and EV/Sales.
PE is one aspect of your portfolio construction to consider when holding or entering into a stock. But it is certainly not the only factor. Take a look at our most recent infographic report on Yirendai for a more in-depth analysis of the stock to help you make a well-informed investment decision. Since we know a limitation of PE is it doesn't properly account for growth, you can use our free platform to see my list of stocks with a high growth potential and see if their PE is still reasonable.
To help readers see pass the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned.