Babe Paley’s St. Regis Apartment, Decorated by Billy Baldwin, Still Enchants

Vogue 1948
Super-swan Barbara Paley nested well. Known as Babe—born a Cushing, later a Mortimer, then finally, famously, the second wife of CBS chairman William S. Paley—she feathered apartments in New York City, a villa in Jamaica, another in the Bahamas, a camp in New Hampshire, and Kiluna Farm, an 85-acre Long Island estate. Kitted out by top decorators (George Stacey, Parish-Hadley, Stéphane Boudin, Billy Baldwin, Natalie Davenport of McMillen), those interiors still divert today, decades after they were dismantled, but one seduces me far more than the others: the 17-foot-by-20-foot Manhattan living room where an evening-gowned Babe—emerging from a cloud of cigarette smoke like a Space Age oracle of Delphi—was photographed for Vogue in 1958 by the future Lord Snowdon.
Like Kiluna Farm, which Bill Paley purchased in 1938, the New York City living room came into Babe’s exquisitely manicured life through marriage. The radio-and-television pioneer separated from his sophisticated first wife, Dorothy, in 1945, and leased a bachelor pad at the St. Regis, the most exquisite of Manhattan’s Belle Époque hotels: three rooms, tenth floor, northwest corner, big windows overlooking Fifth Avenue and East 55th Street, room service. CBS was just four blocks away, and opposite the hotel’s entrance stood Le Pavillon and, later, La Côte Basque, restaurants where the Paleys were regulars. Nobody’s around who can seem to remember a single detail about the pied-à-terre’s pre-Babe decor, but its post-Babe appearance—the Paleys wed in 1947, a marriage that lasted until her death from cancer 31 years later—riveted America when it appeared in Vogue, exhibiting the sublime ministrations of Billy Baldwin of Baldwin and Martin.
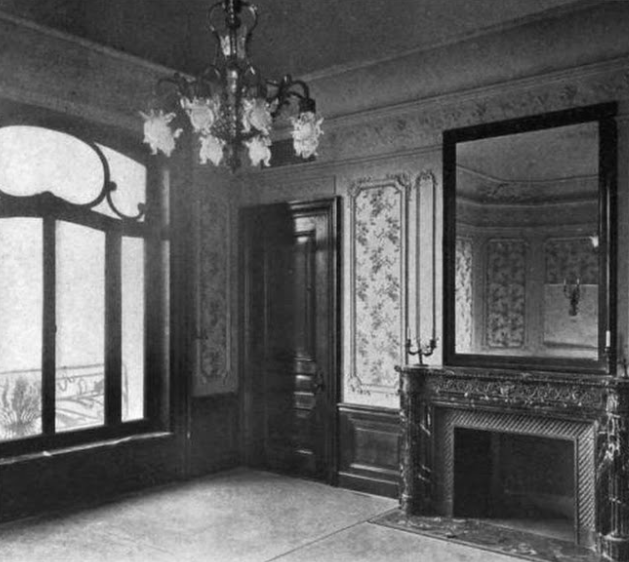

One of the hotel’s Louis XVI–style accommodations—an early magazine article described it as “an ordinary suite”—the apartment’s envelope was pure pastry, piped with curvaceous applied moldings, lacy plaster scrolling, and fussy friezes. The folderol dated from 1904, when the 18-story hotel, designed by architects Samuel Trowbridge and Goodhue Livingston for millionaire John Jacob Astor IV, opened its doors. (It was originally planned as an apartment house, but that concept changed midstream.) As had other St. Regis rooms for the transient rich, the apartment had originally been furnished in a dix-huitième–inspired scheme overseen by Edward Dawson, known as “an authority on period styles” and the head of the upholstery department of Arnold Constable & Company, a top-notch Manhattan department store.

Fashionable reproductions of French furniture suggested Versailles’ private rooms, while other components played fast and loose with historical precision. The Architectural Record gingerly pointed out that the decorators maintained “no very scrupulous adherence to stylistic consistency.” The Louis XVI–style rocking chairs, for example, would have confounded the French court, though the form was surely welcomed by gouty plutocrats relaxing after a Lucullan meal in the St Regis’s gilded main dining room. The dark marble mantels, created by New York’s William H. Jackson Company, were probably the most authentic element in the Louis XVI suites, copied from an 18th-century French original, with many still in place.
Period styles, though, were neither Baldwin’s specialty nor the Paleys’ preference. Still, the decorator once wrote, “If a client wants a nineteenth-century Gothic library, it is up to me to create the best nineteenth-century Gothic library ever done, whether I like it or not.” Like him, the Paleys appreciated European antiques, especially the 18th-century French variety, which was popular in postwar America, and Manhattan’s undisputed power couple avidly shopped for the best examples they could find. They were charismatic fortysomethings, one of whom owned a powerful media empire while the other had been an avatar of chic since her days as a fashion editor at Vogue, in the pages of which she frequently modeled with cool distinction.
“American society women all look alike and spend $700 a dress to do it,” Cuban fashion designer Miguel Ferreras once complained. “They all want to look like Mrs. William Paley.” That meant impeccable and immaculate, not a hair of her Kenneth Battelle bouffant out of place, subtly perfumed (Balmain’s Vent Vert was a favorite), graceful in movement, and reserved in expression. Per Gloria Vanderbilt, “She had edited herself according to her point of view into a mold of perfection and had certainly achieved it in her style, her houses, her garden, her parties, in everything.” Small wonder the National Society of Interior Designers voted Mrs. Paley, in 1964, as “one of the persons who have inspired good design in their environment, influencing public taste throughout the world.” Carped Billy Baldwin, “They are all copying the Paleys.”

Inspired by Napoleon I’s campaign tents and popularized by imperial decorators Percier and Fontaine, romantic tented rooms were having a revival in the 1950s, through the work of tastemakers such as Madeleine Castaing, whom Baldwin admired, and Stéphane Boudin, who helped restore Joséphine Bonaparte’s Château de Malmaison. Since the St. Regis’s architecture could not be changed, camouflaging the planes with fabric was ideal. “It’s great for people who don’t want to invest in repairing their walls,” Baldwin observed. The pâtisserie details disappeared from view, and the curious angle that interrupted the room’s northwest corner was visually blunted. What made the tenting unusual was the material: some 200 yards of Indian calico, a tobacco-brown cotton densely block-printed with pale pink stylized bhuti or flowerheads. Baldwin despised fancy materials. “The word that almost makes me throw up is satin,” he said, facetiously adding that damask actually did make him vomit. Cotton, on the other hand, has “such life, freshness, and variety,” he enthused, noting, “My world is entirely cotton. Inexpensive cotton.” The Paley fabric, source unknown, cost just $2.50 (about $22 today) a yard.
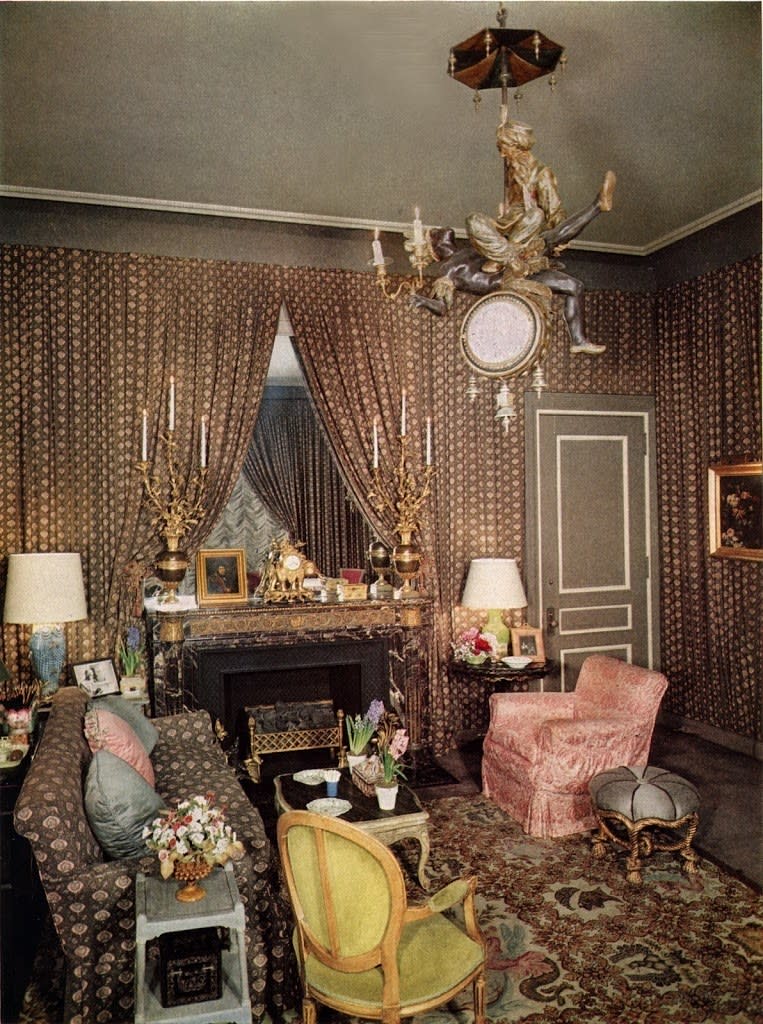

The Indian calico was gathered into long, narrow box pleats (the flattened surface meant that pictures could be hung without compressing the fabric too much) and attached to rods that were fastened beneath the cove cornice (painted a complementary gray-brown) and along the tops of the skirting boards. As in the tented boudoir of Napoléon’s stepdaughter, Hortense, the fabric was strategically parted—the tiebacks were stiff passementerie bows with tassels—revealing the original overmantel mirror and two windows equipped with frothy Austrian shades, the latter being arguably the only design element that would not pass muster today; they always look like fancy knickers. The cotton also covered a custom-made, rolled-arm sofa that was ultimately nicknamed after the Paleys and has remained a constant in deluxe design circles ever since. The ceiling lacked the fabric covering of a traditionally tented room, presumably to keep claustrophobia at bay.

Within this cocoon of rippling texture and dappled motifs, Baldwin established three seating areas—for dining, relaxing, and watching CBS’s latest programming—utilizing contemporary sofas, antique French chairs, what appears to be a Syrie Maugham side table, and some existing hotel decor. The console television was in full view rather than laboriously disguised. “I believe in a mixture of everything,” Baldwin explained, “and by that I mean a mixture of all nationalities, old and new.” Whether old or new, the origins of the room’s unusual needlework rug remain obscure. Theatrically patterned with blackamoors, crowned eagles, grinning satyrs, and spiky amber-brown foliage, and bearing the words "SALVA TELLI," it was found by Babe herself, according to reports.
Baldwin said the rug was a Russian textile known as a Bessarabian, an identification with which a leading Manhattan carpet expert concurs. Another specialist I queried, though, called it “a bizarre piece” that seems to blend various Mediterranean motifs, arguably taken from “a plate or two from some Dekorative Kunst album.” So, perhaps, the carpet wasn’t terribly old at all and maybe not Bessarabian; my gut says Italian, maybe Sicilian. "SALVA TELLI" could be the Italian surname Salvatelli, rather than two separate words, and a Paley family member mentioned something about nuns possibly having stitched it. It’s possible the answer to this mystery lies in Babe’s friendship with jeweler Fulco di Verdura, a Sicilian duke, who made her a double-blackamoor brooch in 1961.
The Paleys also reportedly found the room’s eccentric Orientalist chandelier clock, apparently Venetian, a grace note that art advisor Nicholas B.A. Nicholson calls “a masterpiece.” Its sculptural design depicts two men in apparent combat, the victor seemingly a Turk, the vanquished an allegorical figure representing Africa—a pairing that could reference the Ottoman Empire’s wars in Africa. (The history of the intersection of decorative arts and current events is a rich one.) Then again, Nicholson speculates, “My guess is that Africa is rising, not being attacked. Maybe French, 1881? That’s when the Ottomans lost Tunis to France.”

Candied-almond accent colors, taken from the Indian fabric as well as the carpet, tied the decor together. A slouchy slipcover of pink damask (one of the fabrics that Baldwin said nauseated him) dressed an armchair. Blues, from sky to turquoise, showed up on square silk cushions, a painted two-tier side table, a fish-shape ceramic table lamp, and an enamel cup holding cigarettes that Babe smoked through an ivory holder. Spring-green velvet brightened a fauteuil (the sharp color was repeated in a lamp base), and cherry-red Directoire side chairs attended a small round dining table. Flowered needlework cushions bloomed on a loveseat that was flanked by inviting Victorian-inspired armchairs clad in pale narrow stripes and a bronze rabbit the size of a springer spaniel. Gold discreetly glimmered, from a Napoléon III rope-twist stool (pouf cordes) to an 18th-century ormolu pendule à l’éléphant, a clock resting on the back of a caparisoned pachyderm.
Baldwin described the Paleys’ St. Regis living room as “a Proustian, turn-of-the-century setting,” presumably because of its mondaine intimacy, rather like an aristocratic boudoir, and the eclectic blend of styles and objets de vertu that might have lived happily together in 1890s Paris. To me, it’s an Orientalist fancy out of The Wilder Shores of Love, Lesley Blanch’s biographical study of four real-life Western women who had become entranced by the Middle East in the 19th century. (It was a book that was popular with the ladies who lunch around the time that the Paley apartment was decorated.) The tenting also gave the living room a stage-set ambience, as if the decor could be struck at any moment, thrown on the backs of several camels, and re-erected at another oasis. Which is sort of what happened.
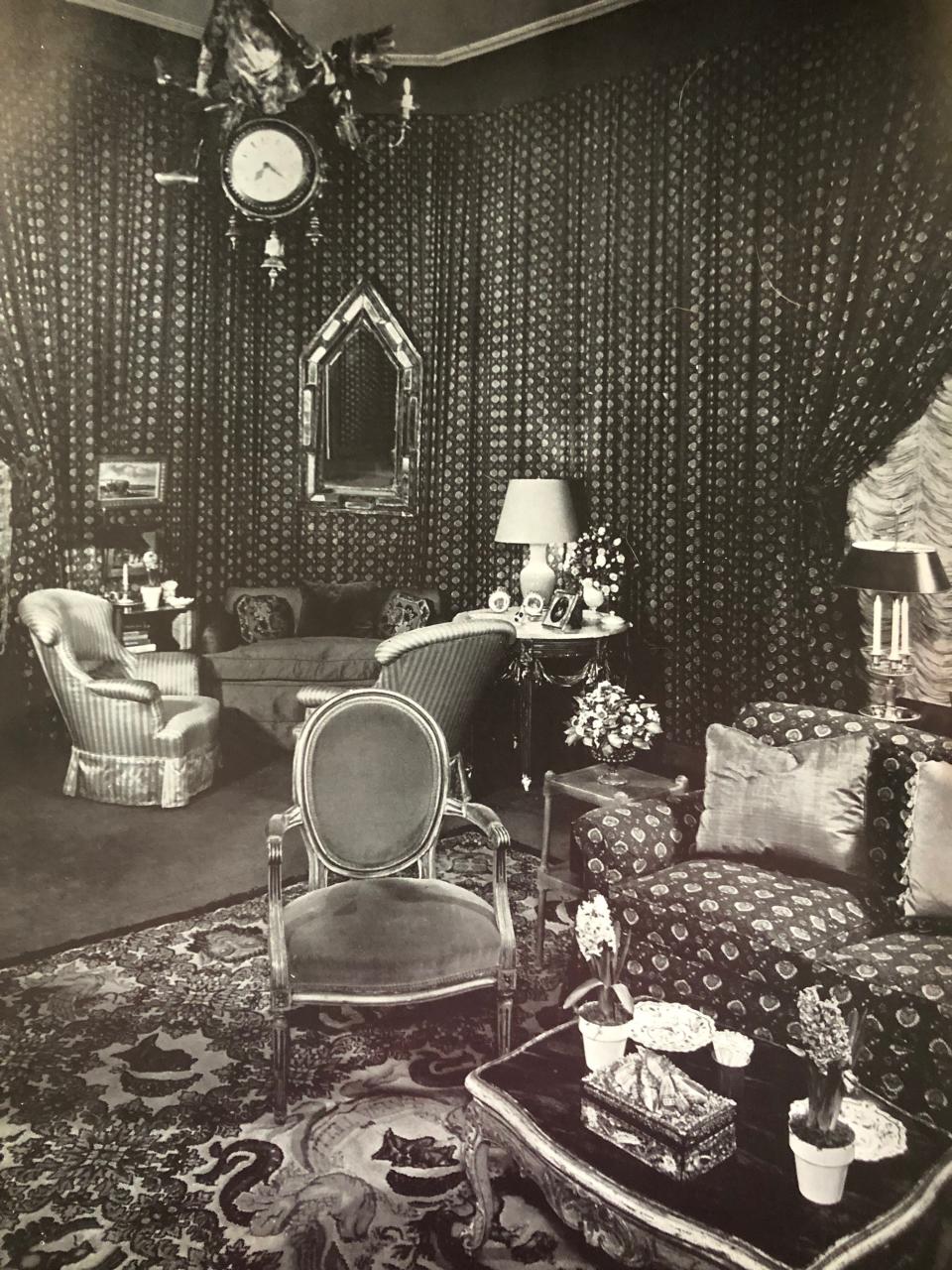
In 1965, the Paleys acquired a 20-room apartment at 820 Fifth Avenue, eight blocks north of the St. Regis, and Baldwin transferred the tented scheme to the new library. Gathered fabric walls (a different paisley pattern this time around) were again on the menu, along with the chandelier clock, carpet, and pendule à l’éléphant. Same ingredients, different outcome. The earlier installation’s irregular, mignon magic simply evaporated in a room of grander scale and conventional proportions, resulting in a handsome space that impressed but did not transport.
Originally Appeared on Architectural Digest
