How Did Select Income REIT’s (NASDAQ:SIR) 4.03% ROE Fare Against The Industry?

Select Income REIT (NASDAQ:SIR) generated a below-average return on equity of 4.03% in the past 12 months, while its industry returned 7.62%. An investor may attribute an inferior ROE to a relatively inefficient performance, and whilst this can often be the case, knowing the nuts and bolts of the ROE calculation may change that perspective and give you a deeper insight into SIR’s past performance. Today I will look at how components such as financial leverage can influence ROE which may impact the sustainability of SIR’s returns. See our latest analysis for Select Income REIT
What you must know about ROE
Return on Equity (ROE) is a measure of Select Income REIT’s profit relative to its shareholders’ equity. An ROE of 4.03% implies $0.04 returned on every $1 invested. While a higher ROE is preferred in most cases, there are several other factors we should consider before drawing any conclusions.
Return on Equity = Net Profit ÷ Shareholders Equity
ROE is assessed against cost of equity, which is measured using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) – but let’s not dive into the details of that today. For now, let’s just look at the cost of equity number for Select Income REIT, which is 10.18%. Given a discrepancy of -6.15% between return and cost, this indicated that Select Income REIT may be paying more for its capital than what it’s generating in return. ROE can be broken down into three different ratios: net profit margin, asset turnover, and financial leverage. This is called the Dupont Formula:
Dupont Formula
ROE = profit margin × asset turnover × financial leverage
ROE = (annual net profit ÷ sales) × (sales ÷ assets) × (assets ÷ shareholders’ equity)
ROE = annual net profit ÷ shareholders’ equity
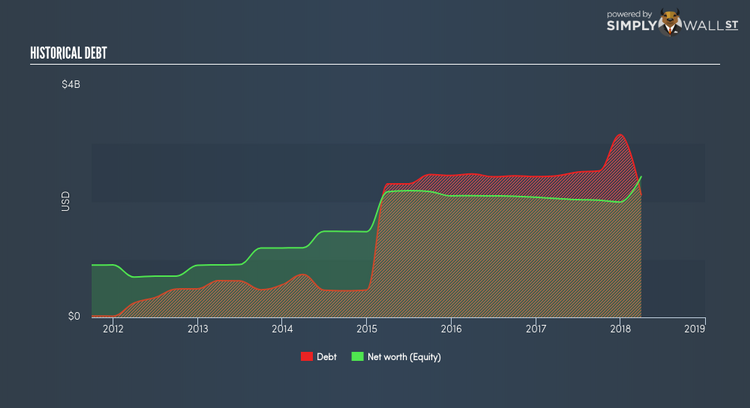
Basically, profit margin measures how much of revenue trickles down into earnings which illustrates how efficient the business is with its cost management. Asset turnover shows how much revenue Select Income REIT can generate with its current asset base. Finally, financial leverage will be our main focus today. It shows how much of assets are funded by equity and can show how sustainable the company’s capital structure is. Since financial leverage can artificially inflate ROE, we need to look at how much debt Select Income REIT currently has. The debt-to-equity ratio currently stands at a sensible 87.09%, meaning the ROE is a result of its capacity to produce profit growth without a huge debt burden.
Next Steps:
While ROE is a relatively simple calculation, it can be broken down into different ratios, each telling a different story about the strengths and weaknesses of a company. Select Income REIT exhibits a weak ROE against its peers, as well as insufficient levels to cover its own cost of equity this year. Although, its appropriate level of leverage means investors can be more confident in the sustainability of Select Income REIT’s return with a possible increase should the company decide to increase its debt levels. Although ROE can be a useful metric, it is only a small part of diligent research.
For Select Income REIT, I’ve put together three essential factors you should further examine:
Financial Health: Does it have a healthy balance sheet? Take a look at our free balance sheet analysis with six simple checks on key factors like leverage and risk.
Valuation: What is Select Income REIT worth today? Is the stock undervalued, even when its growth outlook is factored into its intrinsic value? The intrinsic value infographic in our free research report helps visualize whether Select Income REIT is currently mispriced by the market.
Other High-Growth Alternatives : Are there other high-growth stocks you could be holding instead of Select Income REIT? Explore our interactive list of stocks with large growth potential to get an idea of what else is out there you may be missing!
To help readers see pass the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned.