Examining Genpact Limited’s (NYSE:G) Weak Return On Capital Employed

Today we’ll evaluate Genpact Limited (NYSE:G) to determine whether it could have potential as an investment idea. In particular, we’ll consider its Return On Capital Employed (ROCE), as that can give us insight into how profitably the company is able to employ capital in its business.
First of all, we’ll work out how to calculate ROCE. Then we’ll compare its ROCE to similar companies. Then we’ll determine how its current liabilities are affecting its ROCE.
Return On Capital Employed (ROCE): What is it?
ROCE measures the ‘return’ (pre-tax profit) a company generates from capital employed in its business. In general, businesses with a higher ROCE are usually better quality. Overall, it is a valuable metric that has its flaws. Author Edwin Whiting says to be careful when comparing the ROCE of different businesses, since ‘No two businesses are exactly alike.’
How Do You Calculate Return On Capital Employed?
The formula for calculating the return on capital employed is:
Return on Capital Employed = Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) ÷ (Total Assets – Current Liabilities)
Or for Genpact:
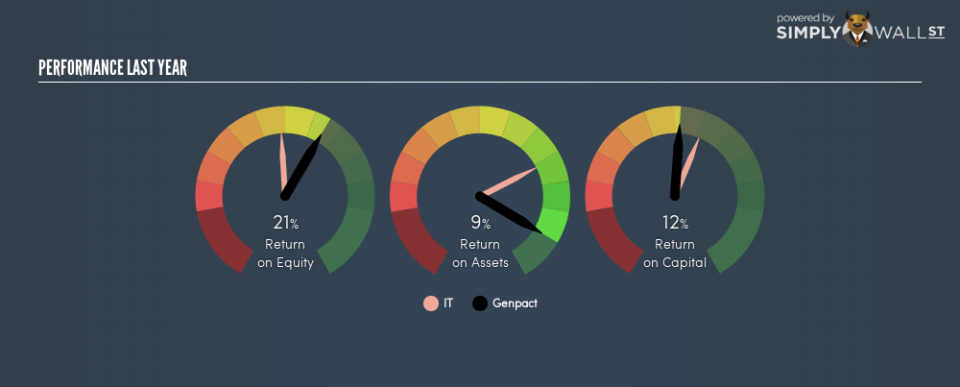
0.12 = US$330m ÷ (US$3.5b – US$1.0b) (Based on the trailing twelve months to September 2018.)
So, Genpact has an ROCE of 12%.
See our latest analysis for Genpact
Want to help shape the future of investing tools and platforms? Take the survey and be part of one of the most advanced studies of stock market investors to date.
Is Genpact’s ROCE Good?
One way to assess ROCE is to compare similar companies. Genpact’s ROCE appears to be substantially greater than the 9.9% average in the IT industry. We would consider this a positive, as it suggests it is using capital more effectively than other similar companies. Independently of how Genpact compares to its industry, its ROCE in absolute terms appears decent, and the company may be worthy of closer investigation.
Remember that this metric is backwards looking – it shows what has happened in the past, and does not accurately predict the future. ROCE can be deceptive for cyclical businesses, as returns can look incredible in boom times, and terribly low in downturns. ROCE is only a point-in-time measure. Future performance is what matters, and you can see analyst predictions in our free report on analyst forecasts for the company.
What Are Current Liabilities, And How Do They Affect Genpact’s ROCE?
Short term (or current) liabilities, are things like supplier invoices, overdrafts, or tax bills that need to be paid within 12 months. Due to the way ROCE is calculated, a high level of current liabilities makes a company look as though it has less capital employed, and thus can (sometimes unfairly) boost the ROCE. To check the impact of this, we calculate if a company has high current liabilities relative to its total assets.
Genpact has total liabilities of US$1.0b and total assets of US$3.5b. Therefore its current liabilities are equivalent to approximately 29% of its total assets. Current liabilities are minimal, limiting the impact on ROCE.
Our Take On Genpact’s ROCE
This is good to see, and with a sound ROCE, Genpact could be worth a closer look. But note: Genpact may not be the best stock to buy. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies with strong recent earnings growth (and a P/E ratio below 20).
If you like to buy stocks alongside management, then you might just love this free list of companies. (Hint: insiders have been buying them).
To help readers see past the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned. For errors that warrant correction please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com.