What Kind Of Shareholders Own New Senior Investment Group Inc. (NYSE:SNR)?

Want to participate in a short research study? Help shape the future of investing tools and you could win a $250 gift card!
A look at the shareholders of New Senior Investment Group Inc. (NYSE:SNR) can tell us which group is most powerful. Insiders often own a large chunk of younger, smaller, companies while huge companies tend to have institutions as shareholders. Companies that used to be publicly owned tend to have lower insider ownership.
New Senior Investment Group is a smaller company with a market capitalization of US$452m, so it may still be flying under the radar of many institutional investors. Our analysis of the ownership of the company, below, shows that institutional investors have bought into the company. Let’s delve deeper into each type of owner, to discover more about SNR.
Check out our latest analysis for New Senior Investment Group
What Does The Institutional Ownership Tell Us About New Senior Investment Group?
Many institutions measure their performance against an index that approximates the local market. So they usually pay more attention to companies that are included in major indices.
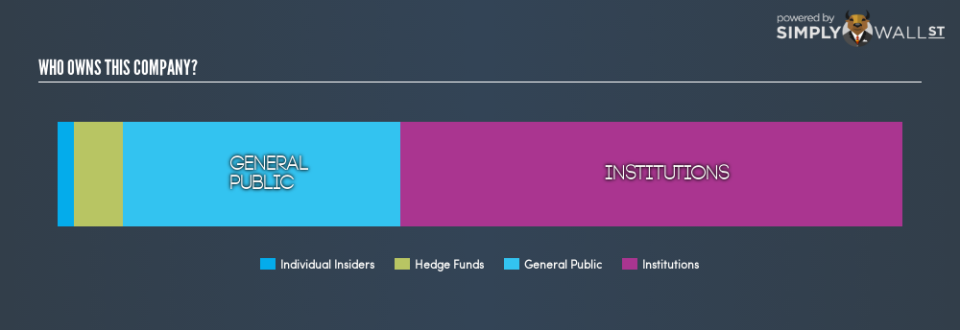
New Senior Investment Group already has institutions on the share registry. Indeed, they own 59% of the company. This can indicate that the company has a certain degree of credibility in the investment community. However, it is best to be wary of relying on the supposed validation that comes with institutional investors. They too, get it wrong sometimes. If multiple institutions change their view on a stock at the same time, you could see the share price drop fast. It’s therefore worth looking at New Senior Investment Group’s earnings history, below. Of course, the future is what really matters.
Since institutional investors own more than half the issued stock, the board will likely have to pay attention to their preferences. Our data indicates that hedge funds own 5.9% of New Senior Investment Group. That worth noting, since hedge funds are often quite active investors, who may try to influence management. Many want to see value creation (and a higher share price) in the short term or medium term. While there is some analyst coverage, the company is probably not widely covered. So it could gain more attention, down the track.
Insider Ownership Of New Senior Investment Group
While the precise definition of an insider can be subjective, almost everyone considers board members to be insiders. Company management run the business, but the CEO will answer to the board, even if he or she is a member of it.
Most consider insider ownership a positive because it can indicate the board is well aligned with other shareholders. However, on some occasions too much power is concentrated within this group.
Shareholders would probably be interested to learn that insiders own shares in New Senior Investment Group Inc.. It has a market capitalization of just US$452m, and insiders have US$9.1m worth of shares, in their own names. This shows at least some alignment. You can click here to see if those insiders have been buying or selling.
General Public Ownership
With a 33% ownership, the general public have some degree of sway over SNR. While this size of ownership may not be enough to sway a policy decision in their favour, they can still make a collective impact on company policies.
Next Steps:
I find it very interesting to look at who exactly owns a company. But to truly gain insight, we need to consider other information, too.
I like to dive deeper into how a company has performed in the past. You can access this interactive graph of past earnings, revenue and cash flow, for free .
If you would prefer discover what analysts are predicting in terms of future growth, do not miss this free report on analyst forecasts.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
To help readers see past the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned. For errors that warrant correction please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com.