What You Must Know About Costco Wholesale Corporation’s (NASDAQ:COST) ROE

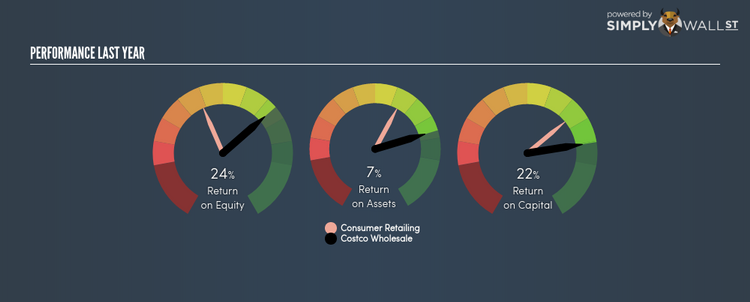
Costco Wholesale Corporation (NASDAQ:COST) delivered an ROE of 23.83% over the past 12 months, which is an impressive feat relative to its industry average of 12.25% during the same period. On the surface, this looks fantastic since we know that COST has made large profits from little equity capital; however, ROE doesn’t tell us if management have borrowed heavily to make this happen. Today, we’ll take a closer look at some factors like financial leverage to see how sustainable COST’s ROE is. View our latest analysis for Costco Wholesale
Breaking down Return on Equity
Firstly, Return on Equity, or ROE, is simply the percentage of last years’ earning against the book value of shareholders’ equity. For example, if the company invests $1 in the form of equity, it will generate $0.24 in earnings from this. Generally speaking, a higher ROE is preferred; however, there are other factors we must also consider before making any conclusions.
Return on Equity = Net Profit ÷ Shareholders Equity
ROE is measured against cost of equity in order to determine the efficiency of Costco Wholesale’s equity capital deployed. Its cost of equity is 8.49%. Given a positive discrepancy of 15.33% between return and cost, this indicates that Costco Wholesale pays less for its capital than what it generates in return, which is a sign of capital efficiency. ROE can be broken down into three different ratios: net profit margin, asset turnover, and financial leverage. This is called the Dupont Formula:
Dupont Formula
ROE = profit margin × asset turnover × financial leverage
ROE = (annual net profit ÷ sales) × (sales ÷ assets) × (assets ÷ shareholders’ equity)
ROE = annual net profit ÷ shareholders’ equity
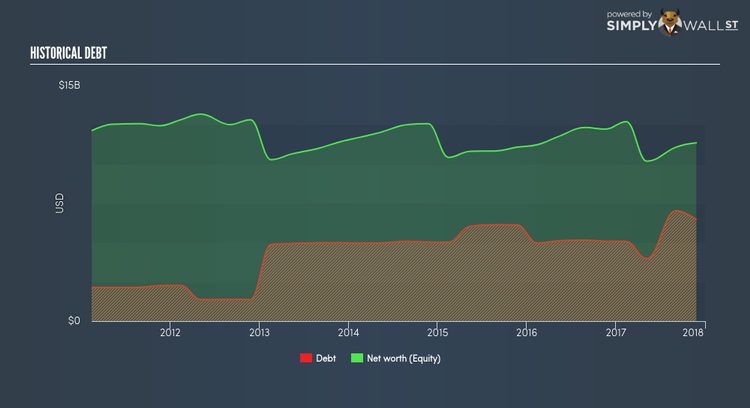
Basically, profit margin measures how much of revenue trickles down into earnings which illustrates how efficient the business is with its cost management. Asset turnover shows how much revenue Costco Wholesale can generate with its current asset base. Finally, financial leverage will be our main focus today. It shows how much of assets are funded by equity and can show how sustainable the company’s capital structure is. Since ROE can be inflated by excessive debt, we need to examine Costco Wholesale’s debt-to-equity level. The debt-to-equity ratio currently stands at a sensible 57.05%, meaning the above-average ROE is due to its capacity to produce profit growth without a huge debt burden.
Next Steps:
ROE is one of many ratios which meaningfully dissects financial statements, which illustrates the quality of a company. Costco Wholesale exhibits a strong ROE against its peers, as well as sufficient returns to cover its cost of equity. ROE is not likely to be inflated by excessive debt funding, giving shareholders more conviction in the sustainability of high returns. ROE is a helpful signal, but it is definitely not sufficient on its own to make an investment decision.
For Costco Wholesale, I’ve compiled three pertinent aspects you should further examine:
1. Financial Health: Does it have a healthy balance sheet? Take a look at our free balance sheet analysis with six simple checks on key factors like leverage and risk.
2. Valuation: What is Costco Wholesale worth today? Is the stock undervalued, even when its growth outlook is factored into its intrinsic value? The intrinsic value infographic in our free research report helps visualize whether Costco Wholesale is currently mispriced by the market.
3. Other High-Growth Alternatives : Are there other high-growth stocks you could be holding instead of Costco Wholesale? Explore our interactive list of stocks with large growth potential to get an idea of what else is out there you may be missing!
To help readers see pass the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned.