Read This Before You Buy Kemper Corporation (NYSE:KMPR) Because Of Its P/E Ratio

Today, we'll introduce the concept of the P/E ratio for those who are learning about investing. We'll apply a basic P/E ratio analysis to Kemper Corporation's (NYSE:KMPR), to help you decide if the stock is worth further research. Kemper has a price to earnings ratio of 12.12, based on the last twelve months. In other words, at today's prices, investors are paying $12.12 for every $1 in prior year profit.
See our latest analysis for Kemper
How Do You Calculate A P/E Ratio?
The formula for P/E is:
Price to Earnings Ratio = Share Price ÷ Earnings per Share (EPS)
Or for Kemper:
P/E of 12.12 = USD75.93 ÷ USD6.27 (Based on the trailing twelve months to September 2019.)
Is A High Price-to-Earnings Ratio Good?
A higher P/E ratio implies that investors pay a higher price for the earning power of the business. All else being equal, it's better to pay a low price -- but as Warren Buffett said, 'It's far better to buy a wonderful company at a fair price than a fair company at a wonderful price'.
How Does Kemper's P/E Ratio Compare To Its Peers?
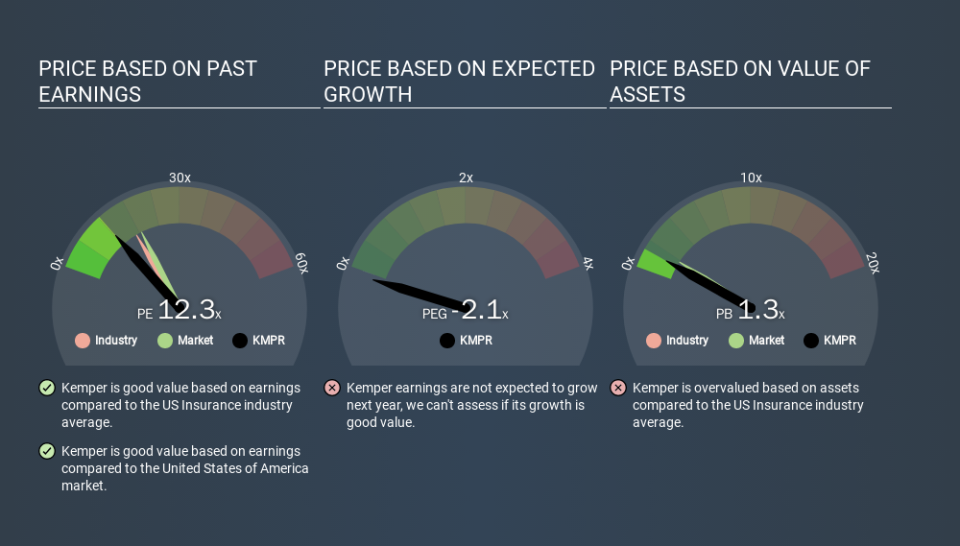
The P/E ratio essentially measures market expectations of a company. The image below shows that Kemper has a lower P/E than the average (17.0) P/E for companies in the insurance industry.
Its relatively low P/E ratio indicates that Kemper shareholders think it will struggle to do as well as other companies in its industry classification. Many investors like to buy stocks when the market is pessimistic about their prospects. If you consider the stock interesting, further research is recommended. For example, I often monitor director buying and selling.
How Growth Rates Impact P/E Ratios
Probably the most important factor in determining what P/E a company trades on is the earnings growth. When earnings grow, the 'E' increases, over time. That means even if the current P/E is high, it will reduce over time if the share price stays flat. A lower P/E should indicate the stock is cheap relative to others -- and that may attract buyers.
In the last year, Kemper grew EPS like Taylor Swift grew her fan base back in 2010; the 57% gain was both fast and well deserved. The sweetener is that the annual five year growth rate of 27% is also impressive. With that kind of growth rate we would generally expect a high P/E ratio.
Don't Forget: The P/E Does Not Account For Debt or Bank Deposits
The 'Price' in P/E reflects the market capitalization of the company. That means it doesn't take debt or cash into account. In theory, a company can lower its future P/E ratio by using cash or debt to invest in growth.
While growth expenditure doesn't always pay off, the point is that it is a good option to have; but one that the P/E ratio ignores.
Is Debt Impacting Kemper's P/E?
Kemper has net debt worth just 7.1% of its market capitalization. So it doesn't have as many options as it would with net cash, but its debt would not have much of an impact on its P/E ratio.
The Verdict On Kemper's P/E Ratio
Kemper's P/E is 12.1 which is below average (18.3) in the US market. The company hasn't stretched its balance sheet, and earnings growth was good last year. If the company can continue to grow earnings, then the current P/E may be unjustifiably low.
When the market is wrong about a stock, it gives savvy investors an opportunity. As value investor Benjamin Graham famously said, 'In the short run, the market is a voting machine but in the long run, it is a weighing machine. So this free visualization of the analyst consensus on future earnings could help you make the right decision about whether to buy, sell, or hold.
Of course, you might find a fantastic investment by looking at a few good candidates. So take a peek at this free list of companies with modest (or no) debt, trading on a P/E below 20.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Thank you for reading.