Teaching tech: how coding moved from the bedroom to the classroom

There are those whose computer screens are bathed in light. These are the consumers - you and me, creating documents with black type on white backgrounds, looking at websites and apps that overflow with jolly colours. The experience is so illuminated that opticians recommend you dim the brightness on your monitor.
Then there are those whose screens are dark. These are the producers, typing line after complex line of code in tiny fonts jutting in from the margin like an arrowhead, each flecked with symbols, slashes, exclamation marks and brackets /!<>. To help them make out this script, which builds the brilliantly lit online world we outsiders see, most coders type in pale fonts on dark backgrounds. Walk into any tech company and you will find them: rows and rows of programmers, staring intently at largely black screens. They are the talent.
Talent, talent, talent. Ask anyone in tech what helps or hinders the development of new companies and they will undoubtedly say: access to talent. What they mean is that there is a global shortage of those capable of founding and then developing new technology companies. And almost any company that launches now is a technology company. If you want to sell something, you must sell it online. If you have supply chains, they will be controlled electronically. If you are in creative industries, from art to fashion to architecture, then your designs will be aided by computers and software. Nothing is totally insulated from the digital revolution.
So the list of the staff required is lengthy, and not always obvious. Start-ups grow very fast, hence your most essential recruit might be an HR manager capable of enlarging a team from two to 200 in 18 months. Other crucial senior execs are known by their acronyms: COO, CTO, CMO - Chief Operating Officer, Chief Technology Officer, Chief Marketing Officer. Product managers are also critical - people with a tech background who also live and breathe the commercial sell.
But the most obvious demand is for those who stare at the black screens: the coders, the software engineers, the developers who express themselves best in secret languages that meaning nothing to the rest of us: Javascript, C++, Python, among many others.

There are an estimated 100,000 plus jobs waiting to be filled in the tech sector, and almost half a million more to come in the next few years. So you would think that Britain’s computer science graduates, of whom we produce about 27,000 each year, would be the hottest ticket in town, in scorching demand from employers. But there is something rotten in the state of Britain’s education system. For six months after leaving university, the graduates with the highest rate of unemployment in this country are those who studied computer science, at nearly 14 per cent. Pharmacologists, by comparison, have just a 3.5 per cent unemployment rate. Nor does the problem disappear over time. According to a 2016 government review by Sir Nigel Shadbolt, unemployment rates for computer scientists three and a half years after leaving higher education is five per cent, almost twice the average. What on earth is going on?
“We need more doing computer science, and we need to make sure that they have the right skills on coming out of university,” says Dr Rachid Hourizi, an academic at the University of Bath who has just been chosen to be the first director of Britain’s new Institute of Coding. The institute was announced by the Prime Minister at Davos, but is an idea that has been hanging around for years, waiting for funding. Last year, 12 months after the Shadbolt review, it finally got it. Hourizi’s mission is clear: “We will produce courses better aligned to industry needs, which will then become the gold standard.”

Opinion varies about just how bad computer science university degrees are in preparing students for the world of work. But the reality is that a host of alternative coding schools have sprung up in an effort to plug the gap. These are often short-term, intensive, usually expensive, immersion courses for those who want to switch careers into tech. One such, Makers’ Academy, whose catchline is “Learn to Code in 12 Weeks”, is run by Evgeny Shadchnev, an engaging young entrepreneur who came from Russia to study for his masters in computer science at Imperial. He then stayed in London and got his first job as a software developer at a marketing agency called Traffic Broker. When he started working, he was shocked. “What I learned on the job is that most of what was expected of me was not covered at university, down to the very basics: how to work as part of a team, how to use version control, and other modern technologies.”
When he had learned the ropes, and had to hire new recruits himself, he found the same problem. “Just like me at the beginning, the graduates I hired had no idea what they were doing.” The choice for Traffic Broker, like most British tech firms, was both binary and unsatisfactory: spend six months and a lot of money hiring someone experienced, or recruit a grad and spend six months hoping they make it to a decent standard.
George Davis ought still to be one of those attending lectures. But the 19-year-old left his computer science course at the University of East Anglia to set up his own business, SenLab, offering predictive analytics of budgets for small and medium sized businesses.
“The degree was actually slowing me down because it was out of date,” he says, from his office in Moorgate, in the heart of the City. “They need to modernise. This is very UK specific. American courses are so much further ahead.”

Rachid Hourizi, it seems, has his work cut out. But his problem is not limited to what students are learning. He also has a huge issue with who the students are in the first place.
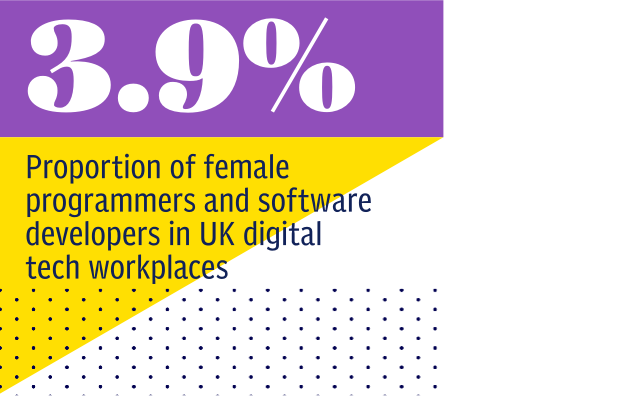
Amali de Alwis used to be what they call a “quant” - a quantitative researcher - which is a bit like being a detective, except that your clues and evidence are buried within statistics and data. It was that background that allowed her to pull some numbers from the Office for National Statistics. She already knew that, of 26,845 individuals accepted onto computer science degrees in 2016, just 14 per cent - 3,775 - were women. But she wanted to see how that tiny cohort got on when they graduated. It turned out that in Britain today, in the tech and telecom industry, female programmers and software developers make up only 3.9 per cent of the workforce. Particularly depressing is that this figure has actually been getting worse - down from 10 per cent a decade ago. Similarly, women made up 20 per cent of computer science students in the early years of this century.
No one is quite sure why. But it seems that, sometime in the last two decades, during which the internet has boomed, women have decided - or been given the impression - that shaping the digital world is not for them. “In digital we have this particularly unpleasant problem around gender diversity,” says Hourizi. “It is morally wrong that we don’t serve everybody, and it’s a waste of talent, which is wrong in practical terms, too. Frankly, it is despicable.”

The ramifications are significant. In an industry struggling to recruit suitable staff, half the population - women - are not even candidates. Moreover, overwhelmingly white, male bias poses commercial problems, too. “Think of early voice recognition software which didn’t recognise women’s voices because they weren’t in the right register,” says de Alwis. Her view is that the best way of building better tech products is to have better representation of women and ethnic minorities working in the groups that build those products. As these become more essential to our daily lives, the importance of doing so only grows. “This is not just about buying a table or a chair,” she says. “Facebook, Twitter, Uber - all of these companies are becoming infrastructure, not just technological tools used by some. If there is bias being built into the systems, we’re taking that bias with us forever. What kind of world do we want to create? Now is the time to say something.”
As AI develops in the next few years, with the growing capacity to derive its own processes, the room for concern only grows. “Technologies are in some sense neutral,” says DeepMind founder Mustafa Suleyman. “They reflect the kind of values and the attitudes and biases and blindspots that we have as creators of those systems.” At the moment, the creators of those systems are overwhelmingly white men.
It is a problem that de Alwis now aims to rectify as head of Code First: Girls, an eight-week coding course for women that aims to get through the basics in 16 hours. It costs £675 for those who can pay; with revenue supporting free courses for the young or just out of education.
On a recent night in an office near Oxford Street, in central London, borrowed from the digital consultancy Transform, 20 or so mostly young women sat around tables in twos and threes. Large screens over their heads displayed the code to allow them to write their names on a webpage. By the end of the course they will have designed an entire website. “The point is to crack their disbelief that they can do it,” says course leader Cedric Kisema, a software developer who volunteers his time.
Students, he says, “come in with nothing”, but, after a lot of homework, and struggles with a fiddly system which tracks every coding change called Git (many students pronounce the name with real feeling until they have cracked it), they are ready to present their work in the final session. In the last course, one produced a dating app site with added suggestions of fun things to do on the dates. “We give a prize to the winner,” says Cedric, noting how, just as in real software development, teamwork is spiced with personal ambition. “There’s real competition to it.”
Among the students was Toni Murphy, 21, a young black psychology student puzzling through Git with her two table-mates, Katerina, 22, and Muhiba, 22. Encouragingly for a discipline which struggles almost as much with ethnic diversity as it does with gender, half the faces were not white. “I had to explain to my mother what I was doing,” said Toni. “But the fact is, I want to understand this stuff. Tech start-up is the smartest thing to do now.”
Code First: Girls has proved increasingly popular. So far, more that 5,000 women have passed through its doors, and it hopes to have trained 20,000 by 2020. In some ways, its success points up the disastrous gender balance of traditional university computer science courses. “By the end of this year, as a small social enterprise, we will be teaching more women to code than go through the entire British higher education system,” says de Alwis. “It’s bonkers.”
Of course, the blame for this malaise cannot be laid exclusively at the door of the higher education system. The problem starts further down the chain, with primary and secondary schools, with parents who do not encourage daughters to consider STEM subjects (science, technology, engineering and maths). It is a failure that riles David Perks, headmaster of the East London Science School (ELSS), a free school set up in 2013.
“It’s not hard,” he insists, in his cramped, cluttered office in The Clock Mill - one of three beautiful Georgian mills on the River Lea - where the school is housed before it moves into new premises, and doubles in size, five years from now. “There’s all the stuff about promoting science to girls. I say just do it. It should be compulsory up to the age of 16.”
At the moment, in STEM subjects, children are only required to take maths and a combined science GCSE. “That’s how little you can get away with. But the chances of you going anywhere with that are nil,” says Perks with derision, pushing a box out of the way to clear some space (it turns out to contain a Celestron Astromaster 130EQ Telescope, kit for the new astronomy GCSE - “Not even Westminster [the public school] offers that,” he laughs.
When Perks began setting up the ELSS in 2012, not a single student from the boroughs of Tower Hamlets or Newham went on to study medicine at university. That’s not because they wouldn’t, it’s because they couldn’t: not one pupil across the two boroughs was pursuing the science A-levels required. Not one.
Today, all children in years 7 and 8 at ELSS study computer science, which has elements of robotics, graphics, coding, and electronics. Some 50 per cent then go on to do it at GCSE. All pupils must do the sciences - physics, chemistry and biology - as separate subjects at GCSE. Craft, design and technology - known as CDT - has been scrapped (Perks: “It’s all making cardboard boxes - a total joke.”) All the girls do physics. “And they are very confident doing it,” says Perks. “They don’t have to be super bright but they must work hard. If they do they will succeed.”
This, it seems, is the crucial point. Science and maths are perceived as being hard subjects. And the educational establishment in the last decade stands accused of diverting students from hard subjects. David Perks himself, as long ago as 2006, set out this charge in a book called: What is Science Education for?
There had been, he wrote, an “underestimation of the capabilities of students, and a desire to protect them from failure, leading to the breaking down of subjects into bite-sized chunks of digestible information at the expense of a deeper appreciation of the whole”.
The result has been catastrophic, according to Stefan Allesch-Taylor, who in 2016 was appointed the first professor of the practice of entrepreneurship at King’s College London, and now mentors students with business ideas. “For the last generation you get a medal for coming last. That is a cancer that will ultimately kill us,” he says.
It’s one reason why, increasingly, those involved in technology are trying to circumvent the traditional education system in this country. For example, Sherry Coutu, she of the trillion-dollar business, now dedicates herself to getting pupils out of schools with her Workfinder app. “If you look at the research,” she says, “90 per cent of teachers say that the best way of boosting student attainment is through work experience. We need a new Dunkirk moment, where small and medium sized business owners open up their doors to work experience, to say to pupils: ‘Hey, this is what it’s like to work because it’s really different to studying.’ Teachers often teach for life and they have hardly any idea about the world of work outside schools.”
That is not the case at Ada sixth form college, in Tottenham, north London. On the wall there are dozens of snapshots of the tech and business executives who have come to speak. And in a nearby classroom, two pupils - Ross Nkama, 18, and Ryan Maugin, 17 - are preparing to join Google as soon as they can. They have apprenticeship interviews with the internet giant the next day, and discuss the best coding language for machine learning with their classmates. The relative merits of C++ and HTML are weighed. The concluding view is that neither is a patch on PyTorch.
Google aren’t concerned with Ryan or Ross’s exam results. Instead they will challenge the boys on their comprehension of computer code; on their own data manipulation coding skills; and give them a logic quiz. Pass this hurdle and a week-long project follows; succeed there and it's a three-year apprenticeship. And this is the decision that many Ada students have to make: university or apprenticeship. The latter, without fees, and with hands-on experience, is increasingly alluring. “I want to focus on computer science now,” says Ross. “And I have a very practical side.”
Nor is Ada concerned with exam results. Instead it recruits students merely with an app-base test, called Lightbot. You can try it yourself. All applicants are interviewed, and 40 per cent have no more than a C-grade average at GCSE.
“We want to attract unusual talent,” says Mark Smith, CEO and founder of the college. “In fact the whole college started a few years ago because I was mentoring a young man called Matthew Banjo, from a humble background, self-taught and brilliant, and he was failing his computer science course because he knew more than his teacher. I tried to get him some proper teaching because I knew that there were tens of thousands of tech vacancies, and that he could go on to an amazing job. Once I saw the mismatch, I realised tech and computing was also a really powerful tool for social mobility.”
Ada, which is routinely cited as a model by tech companies, will move to a new, £31m campus in 2019, with 1,400 students. Smith is then keen to iterate: “We want to grow outside London.” To do so, they need money - its teaching currently costs up to £500,000 per year more than government funds provide. So they raise it themselves from industry. “There’s nothing to stop other schools and academies doing the same,” says Smith, “they just don’t.”
Companies like King, the software firm behind the dizzyingly addictive mobile game, Candy Crush, set up shop on site to offer three-day projects designed to get students working in ways they would if they were actually employees. “Too often, computer science graduates, they can’t present, they can’t work in a team,” says Adam Rogers, Ada’s sixth-form principal. “But they need to, because the stereotypical pale-faced youth sitting alone in a dark room with a keyboard is not the reality in the industry. It’s very collaborative.”

Some universities are trying to change. Abertay, in Dundee, for example, has strong links with Rockstar Games, whose offshoot in Edinburgh, Rockstar North, is famous - or perhaps notorious - for the Grand Theft Auto series. But that is the exception. “A lot of computer science degrees are outdated,” says Rogers. “Students can even avoid programming after one basic module.” No wonder half of Ada’s students now prefer to go straight onto company apprenticeships and skip university altogether.
Britain’s most celebrated technological seer can understand why. James Dyson is, like many US entrepreneurs, a man of imperial drive and ambition. He likes to tell the story of how his breakthrough appliance required more than 5,000 prototypes to develop. Like Jobs and Bezos and Zuckerberg he is near fanatical in his enthusiasm for, and attention to, tiny details of engineering which push established norms of performance. That’s what makes him think he can take on Elon Musk and America’s other big boys in the race to develop electric cars which, sooner or later, will be driverless. You will be able to buy a Dyson car, he promises, within 4 years. Even so, he feels at a critical disadvantage to his rivals across the Atlantic. For, he says, unlike America, where wealth is championed, Britain frowns on successful entrepreneurs and private companies. Perhaps it’s a new-money thing, yet more evidence of the way class wriggles its way into every debate here. In his office at the Dyson headquarters in Malmesbury, the designer, who now lives at Dodington Park, a Grade I-listed estate, rocks his lean, angular frame back and forth in his chair, and bemoans a nation where “making money is rather demonised”, and where “the government tries to extract as much as it can out of companies, requiring more and more red tape and making it less and less attractive for entrepreneurs to start businesses.”
It is to get around another major problem - a lack of suitable talent emerging from our universities - that he has launched the Dyson Institute, a new engineering course that opened its doors to its first 33 students last September. It’s rumoured that Sir James offered the Institute to Oxford University, but was turned down ("utterly unthinkable in America", noted my source). So Dyson went to Warwick University instead, until his programme gets its own degree awarding powers in a couple of years. Not that the Warwick course has gone unchanged. “Traditional curriculums are not dynamic,” says Duncan Piper, Director of the Dyson Institute. “They haven’t changed as much as they could have. We took a lot of the steel and iron ore study out of the Warwick degree and focused on plastics because that’s the future. And we know what is coming because we are building it.”
The model is revolutionary. Dyson students, of whom there will eventually be 200 and whose digs are on the Malmesbury campus, study two days a week, then spend three days on practical product modules: electronic hardware; electronic software; mechanics. They pay no fees. Instead Dyson pays them. The study year lasts 47 weeks, rather than the usual 24 or so. Nor is there a church-and-state division between the academic and the commercial, as there is in so much British higher education. “We’re not afraid of the teaching branding, supply chain, logistics,” says Piper. “Higher education simply does not know what to make of us. There is a nervousness.”
Dyson himself has even been known to pop in and deliver the odd lecture. He says there was “a lot of opposition” from the Russell Group [of top universities] who were “against the concept of people like us starting new universities. And I can well imagine why. I mean, it’s free, and we’re giving our students education from what I believe are the best scientists and engineers in the world.” When asked if the true mark of success will come when a candidate turns down a place at Oxbridge to join the Dyson Institute instead, he replies: “It’s already happened.” The result is a place where, as Piper puts it, “the transition from becoming a graduate to becoming an employee should be pretty seamless”.
The obvious implication is that private companies with the scale and the means, like Google and Dyson, will increasingly take responsibility from universities for their own recruits. There are practical reasons why it makes sense for them: research shows that such home-trained recruits are “stickier”, ie more loyal, and so stay longer. In a highly competitive world, where the best employees are constantly at risk of being poached, that is an enormous bonus. And it is noticeable at Dyson how fanatically dedicated most employees are, not only to the company, but to the man at the top. If you knew nothing about vacuum cleaners, you might think you were entering a benign personality cult whose fetish object is the superpowered electric motor, and that the Dyson Institute was a prime opportunity to indoctrinate valuable new members at a tender, impressionable age. In the best possible way, of course.
The upshot is that Britain’s traditional educational chain - school, university, job - is being broken apart. Companies, particularly those in technology and engineering that require high-end skills, are now routinely teaching their own. But where does that leave those whose education has finished and are in low-skill jobs, or who are not set for academic success and are headed for low-skill jobs that may not exist by the time they emerge from school? After all, on the high street, hundreds of thousands of retail posts are likely to disappear in the coming years, as automation sows mass redundancy in shops and stores. Courses with vision - like those at ELSS, at Ada, or at Makers’ Academy - may be providing some of the answers. The price for failure elsewhere will be high.
“The AI/robotics people say, ‘Well, we’re going to create more jobs than we lose,” says Stefan Allesch-Taylor. “That may be true, but not for the kind of people that you'll be replacing. Because unless you fix our education system - which for low socio-economic groups is dramatically underperforming - then British people just won’t be qualified. We live in a new age now, a world where the mission statement for the next generation will not be to find a job, it will be to create a job. We have to teach them how to do that. It is possible, but it won’t be easy.”
