Why CITIC Limited’s (HKG:267) Return On Capital Employed Might Be A Concern

Today we are going to look at CITIC Limited (HKG:267) to see whether it might be an attractive investment prospect. In particular, we’ll consider its Return On Capital Employed (ROCE), as that can give us insight into how profitably the company is able to employ capital in its business.
First up, we’ll look at what ROCE is and how we calculate it. Next, we’ll compare it to others in its industry. And finally, we’ll look at how its current liabilities are impacting its ROCE.
Return On Capital Employed (ROCE): What is it?
ROCE is a metric for evaluating how much pre-tax income (in percentage terms) a company earns on the capital invested in its business. All else being equal, a better business will have a higher ROCE. Ultimately, it is a useful but imperfect metric. Renowned investment researcher Michael Mauboussin has suggested that a high ROCE can indicate that ‘one dollar invested in the company generates value of more than one dollar’.
So, How Do We Calculate ROCE?
Analysts use this formula to calculate return on capital employed:
Return on Capital Employed = Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) ÷ (Total Assets – Current Liabilities)
Or for CITIC:
0.053 = HK$216b ÷ (HK$7.6t – HK$3.7t) (Based on the trailing twelve months to June 2018.)
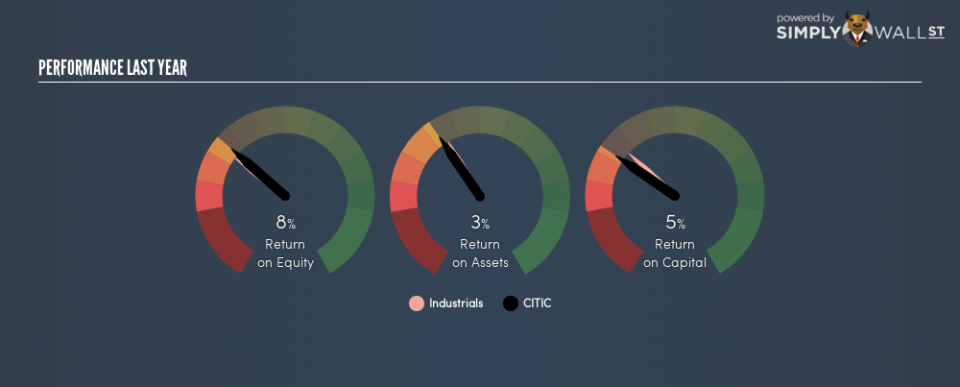
So, CITIC has an ROCE of 5.3%.
View our latest analysis for CITIC
Want to help shape the future of investing tools and platforms? Take the survey and be part of one of the most advanced studies of stock market investors to date.
Does CITIC Have A Good ROCE?
ROCE can be useful when making comparisons, such as between similar companies. CITIC’s ROCE appears to be substantially greater than the 3.9% average in the Industrials industry. We consider this a positive sign, because it suggests it uses capital more efficiently than similar companies. Aside from the industry comparison, CITIC’s ROCE is mediocre in absolute terms, considering the risk of investing in stocks versus the safety of a bank account. Readers may find more attractive investment prospects elsewhere.
It is important to remember that ROCE shows past performance, and is not necessarily predictive. Companies in cyclical industries can be difficult to understand using ROCE, as returns typically look high during boom times, and low during busts. ROCE is, after all, simply a snap shot of a single year. Since the future is so important for investors, you should check out our free report on analyst forecasts for CITIC.
Do CITIC’s Current Liabilities Skew Its ROCE?
Liabilities, such as supplier bills and bank overdrafts, are referred to as current liabilities if they need to be paid within 12 months. The ROCE equation subtracts current liabilities from capital employed, so a company with a lot of current liabilities appears to have less capital employed, and a higher ROCE than otherwise. To check the impact of this, we calculate if a company has high current liabilities relative to its total assets.
CITIC has total assets of HK$7.6t and current liabilities of HK$3.7t. Therefore its current liabilities are equivalent to approximately 49% of its total assets. CITIC’s ROCE is improved somewhat by its moderate amount of current liabilities.
What We Can Learn From CITIC’s ROCE
Despite this, its ROCE is still mediocre, and you may find more appealing investments elsewhere. But note: CITIC may not be the best stock to buy. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies with strong recent earnings growth (and a P/E ratio below 20).
I will like CITIC better if I see some big insider buys. While we wait, check out this free list of growing companies with considerable, recent, insider buying.
To help readers see past the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned. For errors that warrant correction please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com.