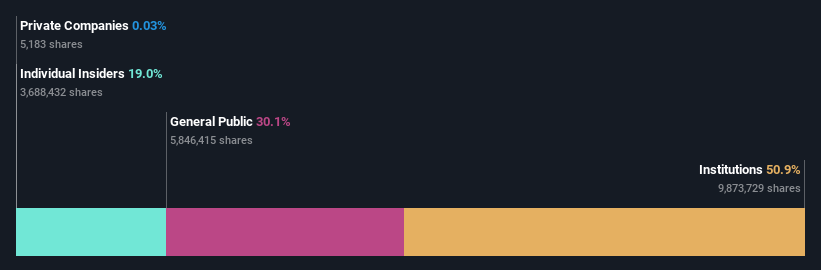
The Cato Corporation (NYSE:CATO) is a favorite amongst institutional investors who own 51%
Key Insights
Given the large stake in the stock by institutions, Cato's stock price might be vulnerable to their trading decisions
The top 11 shareholders own 50% of the company
If you want to know who really controls The Cato Corporation (NYSE:CATO), then you'll have to look at the makeup of its share registry. We can see that institutions own the lion's share in the company with 51% ownership. That is, the group stands to benefit the most if the stock rises (or lose the most if there is a downturn).
Since institutional have access to huge amounts of capital, their market moves tend to receive a lot of scrutiny by retail or individual investors. Hence, having a considerable amount of institutional money invested in a company is often regarded as a desirable trait.
Let's take a closer look to see what the different types of shareholders can tell us about Cato.
See our latest analysis for Cato
What Does The Institutional Ownership Tell Us About Cato?
Institutional investors commonly compare their own returns to the returns of a commonly followed index. So they generally do consider buying larger companies that are included in the relevant benchmark index.
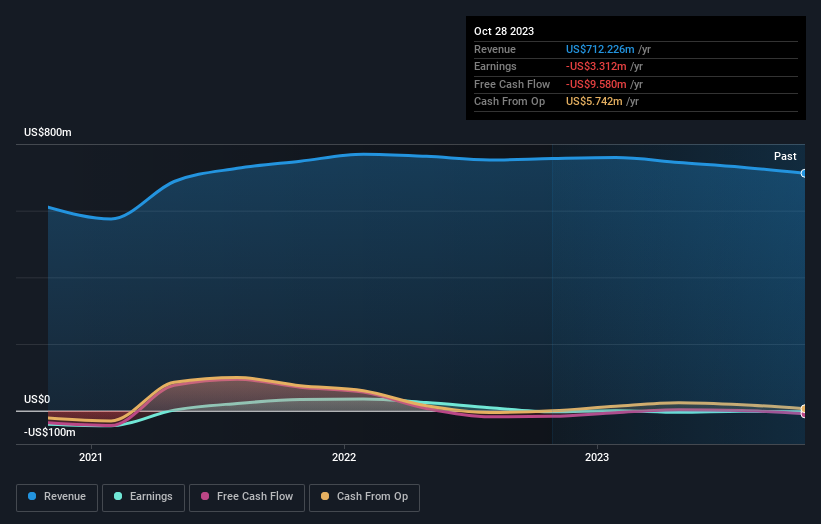
We can see that Cato does have institutional investors; and they hold a good portion of the company's stock. This can indicate that the company has a certain degree of credibility in the investment community. However, it is best to be wary of relying on the supposed validation that comes with institutional investors. They too, get it wrong sometimes. It is not uncommon to see a big share price drop if two large institutional investors try to sell out of a stock at the same time. So it is worth checking the past earnings trajectory of Cato, (below). Of course, keep in mind that there are other factors to consider, too.
Investors should note that institutions actually own more than half the company, so they can collectively wield significant power. Hedge funds don't have many shares in Cato. With a 15% stake, CEO John P. Cato is the largest shareholder. Meanwhile, the second and third largest shareholders, hold 7.0% and 6.1%, of the shares outstanding, respectively.
A closer look at our ownership figures suggests that the top 11 shareholders have a combined ownership of 50% implying that no single shareholder has a majority.
While it makes sense to study institutional ownership data for a company, it also makes sense to study analyst sentiments to know which way the wind is blowing. As far as we can tell there isn't analyst coverage of the company, so it is probably flying under the radar.
Insider Ownership Of Cato
The definition of an insider can differ slightly between different countries, but members of the board of directors always count. The company management answer to the board and the latter should represent the interests of shareholders. Notably, sometimes top-level managers are on the board themselves.
I generally consider insider ownership to be a good thing. However, on some occasions it makes it more difficult for other shareholders to hold the board accountable for decisions.
It seems insiders own a significant proportion of The Cato Corporation. Insiders have a US$25m stake in this US$131m business. It is great to see insiders so invested in the business. It might be worth checking if those insiders have been buying recently.
General Public Ownership
The general public, who are usually individual investors, hold a 30% stake in Cato. This size of ownership, while considerable, may not be enough to change company policy if the decision is not in sync with other large shareholders.
Next Steps:
It's always worth thinking about the different groups who own shares in a company. But to understand Cato better, we need to consider many other factors. For instance, we've identified 2 warning signs for Cato that you should be aware of.
Of course this may not be the best stock to buy. So take a peek at this free free list of interesting companies.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.