Should We Worry About Hasbro, Inc.'s (NASDAQ:HAS) P/E Ratio?

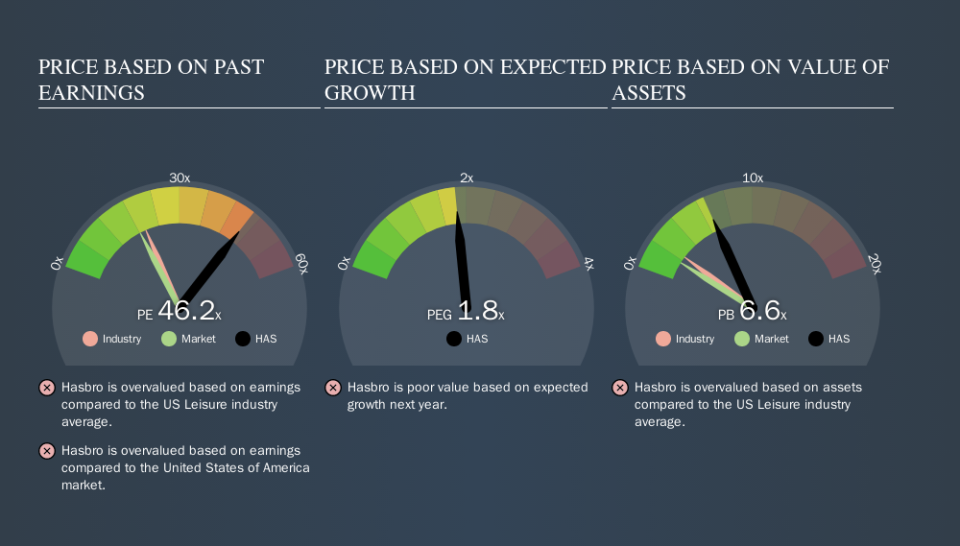
Today, we'll introduce the concept of the P/E ratio for those who are learning about investing. We'll show how you can use Hasbro, Inc.'s (NASDAQ:HAS) P/E ratio to inform your assessment of the investment opportunity. Hasbro has a price to earnings ratio of 46.24, based on the last twelve months. That corresponds to an earnings yield of approximately 2.2%.
Check out our latest analysis for Hasbro
How Do I Calculate Hasbro's Price To Earnings Ratio?
The formula for price to earnings is:
Price to Earnings Ratio = Share Price ÷ Earnings per Share (EPS)
Or for Hasbro:
P/E of 46.24 = $95.79 ÷ $2.07 (Based on the trailing twelve months to September 2019.)
Is A High Price-to-Earnings Ratio Good?
The higher the P/E ratio, the higher the price tag of a business, relative to its trailing earnings. That isn't necessarily good or bad, but a high P/E implies relatively high expectations of what a company can achieve in the future.
How Does Hasbro's P/E Ratio Compare To Its Peers?
One good way to get a quick read on what market participants expect of a company is to look at its P/E ratio. The image below shows that Hasbro has a higher P/E than the average (19.9) P/E for companies in the leisure industry.
That means that the market expects Hasbro will outperform other companies in its industry. The market is optimistic about the future, but that doesn't guarantee future growth. So investors should always consider the P/E ratio alongside other factors, such as whether company directors have been buying shares.
How Growth Rates Impact P/E Ratios
Companies that shrink earnings per share quickly will rapidly decrease the 'E' in the equation. Therefore, even if you pay a low multiple of earnings now, that multiple will become higher in the future. So while a stock may look cheap based on past earnings, it could be expensive based on future earnings.
Hasbro increased earnings per share by a whopping 26% last year. Unfortunately, earnings per share are down 6.5% a year, over 5 years.
Don't Forget: The P/E Does Not Account For Debt or Bank Deposits
It's important to note that the P/E ratio considers the market capitalization, not the enterprise value. In other words, it does not consider any debt or cash that the company may have on the balance sheet. The exact same company would hypothetically deserve a higher P/E ratio if it had a strong balance sheet, than if it had a weak one with lots of debt, because a cashed up company can spend on growth.
Spending on growth might be good or bad a few years later, but the point is that the P/E ratio does not account for the option (or lack thereof).
So What Does Hasbro's Balance Sheet Tell Us?
Hasbro has net debt worth just 5.1% of its market capitalization. So it doesn't have as many options as it would with net cash, but its debt would not have much of an impact on its P/E ratio.
The Bottom Line On Hasbro's P/E Ratio
Hasbro's P/E is 46.2 which is above average (18.3) in its market. The company is not overly constrained by its modest debt levels, and its recent EPS growth very solid. So on this analysis it seems reasonable that its P/E ratio is above average.
When the market is wrong about a stock, it gives savvy investors an opportunity. People often underestimate remarkable growth -- so investors can make money when fast growth is not fully appreciated. So this free visualization of the analyst consensus on future earnings could help you make the right decision about whether to buy, sell, or hold.
Of course you might be able to find a better stock than Hasbro. So you may wish to see this free collection of other companies that have grown earnings strongly.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.